DNS TTL: Your Ultimate Guide To Time To Live For Fast Websites
Ever wondered how the seemingly simple act of typing a website address into your browser translates into the instantaneous appearance of a webpage? The unsung hero of this process, often overlooked, is the Time To Live (TTL) value in the Domain Name System (DNS), and understanding its intricacies is key to a smooth and efficient online experience.
At its core, the TTL value is a fundamental setting that dictates the operational efficiency of the internet. It's a mechanism that impacts both the speed at which you access your favorite websites and the reliability of the entire DNS infrastructure. To truly grasp the intricacies of the internet and enhance your digital experience, a close look at TTL values is crucial.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | TTL stands for "Time To Live" and refers to the duration, in seconds, that a DNS resolver caches a DNS record before requesting a fresh copy. |
| Function | The TTL value tells DNS resolvers how long they can store a specific DNS record in their cache. This affects how often the resolver needs to query the authoritative DNS server for updates. |
| Impact on Speed | Longer TTL values can speed up website access by reducing the number of DNS queries. However, longer TTLs mean updates to DNS records take longer to propagate. |
| Impact on Reliability | Shorter TTL values ensure DNS records are up-to-date, improving reliability. However, they can lead to increased query traffic. |
| Typical Range | Commonly, TTL values range between 300 seconds (5 minutes) and 86,400 seconds (24 hours). |
| Factors to Consider | The optimal TTL value depends on how frequently DNS records change. Websites with frequent updates may use shorter TTLs. |
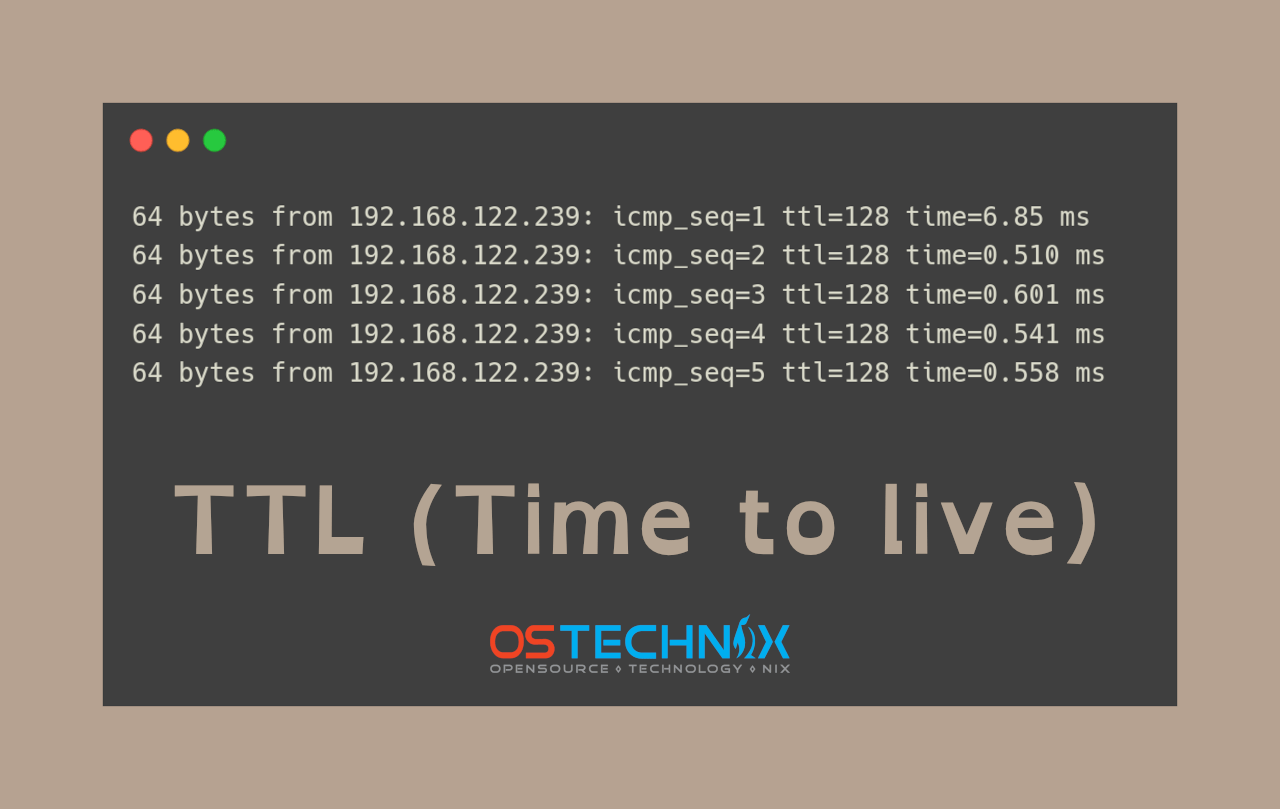
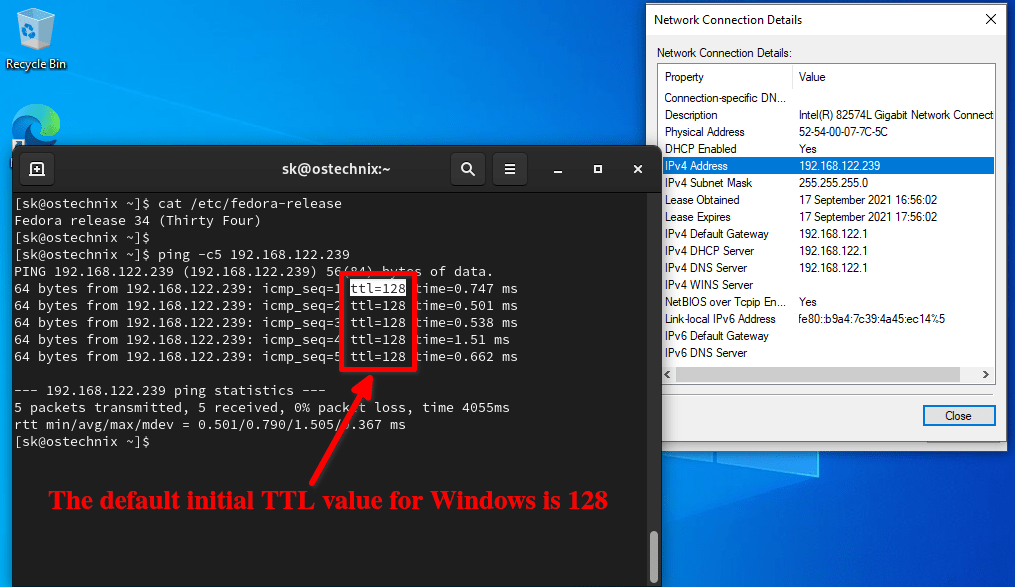
| Tools for Checking | You can check a site's current TTL using tools like `dig` or `nslookup` in your terminal or command prompt. |
| Security Implications | Longer TTLs can make sites more vulnerable to DNS hijacking or cache poisoning. |
| Advanced Techniques | Advanced techniques include split-horizon DNS and DNS load balancing. |
| Integration | TTL values interact with CDNs for enhanced performance. |
| Troubleshooting | Common issues are slow propagation and outdated records, addressed by adjusting TTLs or optimizing DNS. |
| Best Practices | Use shorter TTLs during migrations. Monitor DNS performance. Test for optimal balance. |
So, what exactly is this 'Time To Live' in the context of DNS? In its simplest form, TTL is a digital timer that determines how long a DNS resolver, such as the one provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a public DNS server like Google's, will cache a specific DNS record before it needs to ask for a fresh copy from the authoritative DNS server. This server, in turn, holds the master records for a particular domain. Think of it as an expiry date for information cached on the web, playing a pivotal role in how quickly you can access websites and how reliably those sites can be accessed.
Consider your first encounter with a new website. When you type its address, your device starts by asking a DNS resolver for the site's IP address. The resolver first checks its cache; if the information isn't there, it goes to the authoritative DNS server to fetch it. This is where TTL comes into play. The resolver then stores the IP address for the amount of time specified by the TTL value. So, when you revisit the site within that period, the resolver pulls the IP address from its cache instead of making a fresh query to the authoritative server. This efficiency translates directly to faster loading times.
The importance of the TTL value is twofold: it directly impacts the speed and reliability of your online experience. Shorter TTL values mean the DNS records are updated more frequently, ensuring you always have the latest information. This is vital if a website is moving servers or making changes. Conversely, longer TTL values accelerate access by decreasing the number of queries. However, this can result in "stale" data if changes aren't reflected quickly enough. This presents a balancing act. The goal is to strike a good balance. If the TTL value is long enough, everything stays quick and seamless. If it's short enough, the site stays up-to-date.
Now, lets delve into some frequently asked questions concerning these critical TTL values. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned web professional, these insights should clear up any confusion you might have.
What constitutes a 'good' TTL value? The ideal TTL value is not one-size-fits-all; it depends on your unique situation. For the majority of websites, a TTL setting that falls between 300 seconds (or 5 minutes) and 86,400 seconds (or 24 hours) works well. Websites that undergo frequent updates to their DNS records will benefit from a shorter TTL. Conversely, if your DNS records remain relatively static, you can afford to utilize a longer TTL.
Can TTL values be set too long? Absolutely. While an extremely long TTL can conserve query traffic, any adjustments you make to your DNS records will take longer to propagate. Consequently, outdated information could be displayed to users, which is undesirable, particularly if you're in the midst of migrating servers or implementing significant modifications.
What transpires when a TTL expires? As the TTL timer reaches zero, the DNS resolver becomes aware that it is time to obtain a fresh copy of the DNS record from the authoritative server. This procedure ensures the information remains current and accurate, functioning much like clicking the refresh button on your web browser to get the most recent iteration of a webpage.
Let's explore some essential best practices to leverage TTL values effectively. Keep these in mind when configuring your DNS:
- Set a reasonable TTL duration based on the frequency of updates to your DNS records.
- Employ shorter TTLs during DNS migrations or when you're making frequent updates.
- Monitor your DNS performance to understand how different TTL values affect both speed and reliability.
- Experiment with various TTL configurations to identify the best balance that aligns with your specific requirements.
How can you ascertain your current TTL setting? You can easily check your current TTL value using utilities such as 'dig' or 'nslookup'. All you need to do is open your terminal or command prompt and type 'dig yourdomain.com'. Then, examine the output for the TTL value, usually found within the ANSWER SECTION. Its that simple!
The impact of TTL on website performance is significant. A well-configured TTL can reduce latency, thereby decreasing the number of DNS queries required. This reduction translates into faster loading times for your visitors, a critical factor in user satisfaction and SEO ranking. On the other hand, an improperly configured TTL might result in slow loading times or even downtime if updates arent promptly disseminated. Website speed and performance are greatly impacted by TTL value. When configured correctly, TTL can minimize latency by reducing the number of required DNS queries.
DNS propagation is the process of updating DNS records across all resolvers across the globe. Implementing a shorter TTL expedites this process, ensuring changes are reflected more quickly. However, it can increase query traffic. The aim is to find the most optimal balance for the specific requirements of your website.
Although TTL primarily influences performance, it also has security implications. Longer TTLs can render your site more vulnerable to security breaches such as DNS hijacking or cache poisoning. This can happen because outdated or malicious records may persist longer in caches. Thus, while optimizing for speed, security should always be a top priority.
Can a well-configured TTL help prevent DDoS attacks? Not directly, but it can indeed help reduce the load on your DNS servers by minimizing the number of queries. This can partially mitigate the effects of a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack by preventing your DNS infrastructure from being overwhelmed with requests. A well-tuned TTL can also reduce latency by minimizing the number of DNS queries required.
If you are ready to elevate your TTL strategy, consider these advanced techniques:
- Employ split-horizon DNS to establish distinct TTL values for internal and external queries.
- Implement DNS load balancing to distribute traffic more effectively.
- Continuously monitor DNS performance metrics to refine your TTL settings over time.
Employing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can further enhance the advantages of a well-configured TTL. CDNs cache content nearer to your users, additionally decreasing latency. By integrating a strategic TTL approach with CDN caching, you can create a user experience that is both exceptionally fast and reliable.
Even the most meticulously planned strategies may occasionally falter. If you encounter issues with your TTL values, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Carefully review your DNS settings to ensure TTL values are accurately set.
- Monitor DNS query logs to identify any unusual patterns or potential errors.
- Experiment with different TTL values to assess if they improve performance or resolve any existing problems.
Some prevalent TTL-related issues include slow propagation, outdated records, and excessive query traffic. Possible solutions involve modifying your TTL values, optimizing your DNS configuration, or transitioning to a more reliable DNS provider.
In summary, you now have a comprehensive understanding of TTL values and their influence on your website's performance. Whether you're refining your DNS settings or addressing problems, grasping TTL is fundamental to keeping your site running efficiently. Now, take action. Evaluate your current TTL settings, test different configurations, and gauge their effects on your site's speed and dependability. Be sure to share your experiences in the comment section or reach out via social media. The discussion never ends, as we work to improve! To continue learning, explore our other articles on all matters concerning technology and DNS. There is always more to learn, and we are here to support you throughout this journey.
Reference: Cloudflare

Detail Author:
- Name : Imogene Block
- Username : hiram.kuvalis
- Email : white.noe@kunde.biz
- Birthdate : 1980-10-02
- Address : 349 Eva Coves Apt. 464 North Lula, NC 56816
- Phone : +14699845102
- Company : Jacobi-Wilkinson
- Job : Oil Service Unit Operator
- Bio : Voluptates quidem in sit aperiam. Dolores quis reiciendis ut id minus rerum. Laboriosam fuga aliquam laudantium in sunt. Facilis velit autem culpa qui debitis.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@skuhlman
- username : skuhlman
- bio : Veniam assumenda ipsa ea dolores.
- followers : 3119
- following : 165
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/stefaniekuhlman
- username : stefaniekuhlman
- bio : Voluptatem ut voluptatem quis recusandae quidem et maiores. Sapiente labore aut quaerat vero officiis illum et.
- followers : 501
- following : 660